Academy
How does the crawler work?
Imagine the internet as a great spider web on which the god Google would launch an army of robotic spiders (hence the names Web and Spider) in order to discover all the sites therein.
After having analyzed and recorded the content of each page discovered, the crawlers report their information back to Google, who registers the information in a large book called the Index.

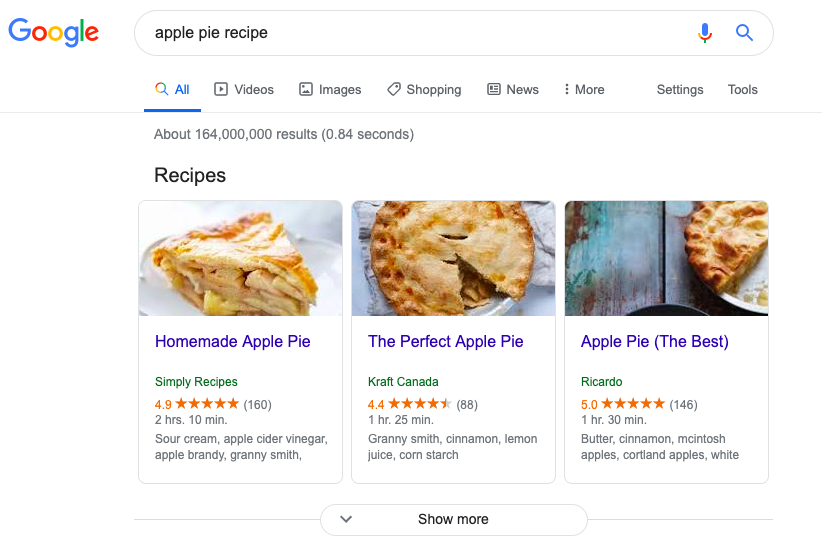
When you search on Google, it’s not the internet you’re searching, it’s the Google index. If you search for the keyword “apple pie recipe“, Google will tell you that it has discovered 164,000,000 pages in its index that mention “apple pie recipe”, and all of that takes only 0.84 seconds … Impressive.
What is Google doing with the information that Googlebots provide?
Spider information is stored in Google’s memory and used to provide ‘’Search Engine Result Pages, commonly known as SERP. These are the results that Google presents in large blue letters during a search.
Of course, Google’s algorithm is extremely complex, but in its simplest form, Google is really just a model detection program. When you search for a keyword (this is the name of the word or words you use to do your research), Google will provide you with a list of websites corresponding to the model associated with your search.
So if in my pie search, I had written “apple pie” instead of “apple pie recipe” as a keyword, the result would have been similar, but slightly different, and this is because Google would not have used the same keyword to do its research. So the model, ie. the letters of the keyword I searched for, was different and had a more generic character. In addition to all apple pie recipes, Google will also offer me a multitude of other pages that will talk about apple scented perfumes, stories about apple pie, pictures referring to apple pie or a simple blog that talks about crawlers…
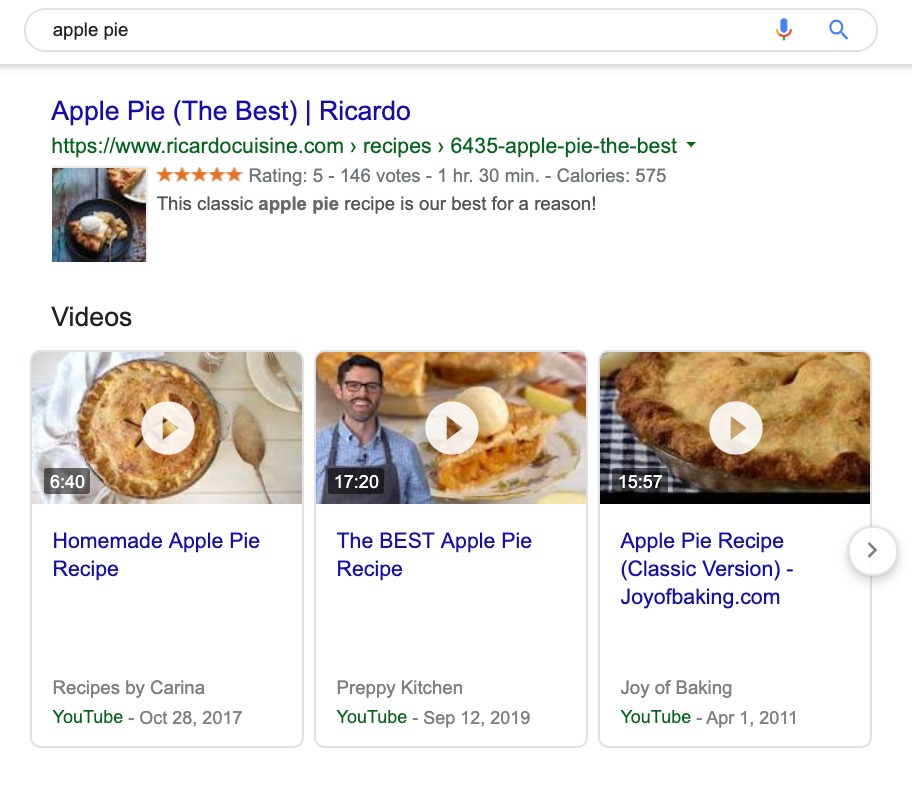
We see that for the new search, as we should expect, the number of pages proposed increased from 164 million to 306 million.
The majority of people do not realize that when they search on Google, they are not really searching the Web. In fact, they are searching Google’s web index … the stored copy of the sites that Google has been exploring. Googlebots are the tool used by Google to discover the content of Web sites. Basically, a spider will start on one page and extract all the content from this page, then follow the links to other pages attached to it. Then, it follows the links on these pages again to discover even more content, and so on …
The spiders continue to travel at a bewildering speed until most of the websites have been explored. Note that there are more than 30 trillion Google-indexed web pages today … As spiders explore all these pages, a copy is stored on Google’s servers. This is where the rankings come in – and this is where the SEO work begins. Google uses an algorithm to view the list of pages extracted from the index and to rank the pages according to their relevance. In our search for “Apple pie recipe” – Google searched the index and created a list of all the websites with an apple pie recipe. Then, it used its algorithm to sort this list so that the most relevant sites are found at the top of the list.
What are the limitations of Google’s index?
Google’s index will only detect the pages that we want to show. If the programmer of a site does not want Google to index certain pages of his site, he will only have to indicate it with the term no-index in his code. Also, if by mistake you create a web page that is not linked to your site, what is called in the jargon an orphan page, the crawlers will not have the “thread” of the web that will take them to the page so it will risk being ignored by Google. A site well done is a site where all the pages are connected to one another.
Finally, the most important limitation of Google’s index is the time between each indexing for sites that are there. Let’s say I make a change on this page and instead of apple pie, I decide to use the keyword “banana cake” in my example. Well, until Googlebots visit me again, I’ll continue to appear in the index when I’m searching for apple pie. Even worse if I decided to delete this page and replace it with a different URL, users could still go there, but they would face code 404, page not found.
There are hundreds of ranking factors in Google’s algorithm, each with a different weight or assigned value. The algorithm examines a few hundred factors that influence the rank that will be assigned to a page (its relevance), such as its content, the number of other sites linked to that page, and the quality of the website.
When we do SEO, we try to influence these relevance scores. We know that if we optimize the right signals, Google’s algorithm will decide that the page is most relevant – and that it offers one of the best answers to the question – so Google will display this page earlier in the SERP.
Learn how to influence the position of a website’s pages in the Google index on our SEO Académy page.
For more information, here’s a video of our friends at Google!
Eric St-Cyr
Leader ProStarSEO
[email protected]
581 447 4376